 |
 |
| J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent > Volume 41(3); 2014 > Article |
мҙҲлЎқ
ліё м—°кө¬лҠ” м ң2лҢҖкө¬м№ҳк№Ңм§Җ кө¬к°• лӮҙм—җ 맹м¶ңн•ҳм—¬ 비көҗм Ғ м•Ҳм •лҗң көҗн•©мқ„ мқҙлЈЁкё° мӢңмһ‘н•ң мҳҒкө¬м№ҳм—ҙкё° мІӯмҶҢл…„мқҳ л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқ„ м•Ңм•„ліҙкі мһҗ н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. м „лқјл¶ҒлҸ„ мқөмӮ°мӢң мҶҢмһ¬мқҳ 2к°ң мӨ‘н•ҷкөҗ н•ҷмғқ 385лӘ…мқ„ лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң мӢңн–үн•ң кө¬к°•кІҖ진мқ„ нҶөн•ҙ м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳмҷҖ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҘј мЎ°мӮ¬н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
мЎ°мӮ¬ лҢҖмғҒ мІӯмҶҢл…„мқҳ м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳлҠ” нҸүк· 12.42м җ, мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” нҸүк· 2.89к°ңлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ. көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢк°Җ л§Өмҡ° н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨкі нҢҗлӢЁлҗҳлҠ” м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 36м җ мқҙмғҒмқҖ 4лӘ…(1.03%)мқҙм—Ҳмңјл©°, лӮЁн•ҷмғқмқҙ м—¬н•ҷмғқм—җ 비н•ҙ мғҒм•… мӨ‘м Ҳм№ҳмқҳ м •мӨ‘мқҙк°ңмҷҖ н•ҳм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҲҳнҸүн”јк°ңлҘј лӮҳнғҖлӮҙлҠ” 비мңЁмқҙ мң мқҳн•ҳкІҢ лҶ’м•ҳлӢӨ(p < 0.05). м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳлҘј кө¬м„ұн•ҳлҠ” 10к°ң н•ӯлӘ© мӨ‘ 7к°ң н•ӯлӘ©(кІ°мҶҗм№ҳм•„ мҲҳ, м „м№ҳл¶Җ м•…к¶Ғ мҙқмғқлҸ„, мғҒм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мөңлҢҖ ліҖмң„лҹү, н•ҳм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мөңлҢҖ ліҖмң„лҹү, н•ҳм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҲҳнҸүн”јк°ңлҹү, м „м№ҳл¶Җ к°ңл°©көҗн•©, м ң1лҢҖкө¬м№ҳмқҳ м „нӣ„л°© кҙҖкі„)м—җм„ң к°Ғ н•ӯлӘ©мқҳ м •мғҒ лІ”мЈјм—җ мҶҚн•ҳлҠ” 집лӢЁм—җ 비н•ҙ м •мғҒ лІ”мЈјм—җм„ң лІ—м–ҙлӮң 집лӢЁмқҳ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳк°Җ мң мқҳн•ҳкІҢ лҶ’м•ҳлӢӨ(p< 0.05).
лӘ…л°ұн•ң л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мЎҙмһ¬к°Җ мқём •лҗҳлҠ” м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 26м җмқ„ кё°мӨҖмңјлЎң, 26м җ лҜёл§Ңм—җ 비н•ҙ 26м җ мқҙмғҒмқё 집лӢЁмқҳ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳк°Җ лҶ’м•ҳмңјл©°(p < 0.01), м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳмҷҖ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳ мӮ¬мқҙм—җ мң мқҳн•ң м„ нҳ• мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„к°Җ лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ(r = 0.584, p < 0.01).
мқҙмғҒмқҳ кІ°кіјлЎңл¶Җн„° мІӯмҶҢл…„мқҳ л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқ мң лі‘лҘ мӮ¬мқҙм—җ мң мқҳн•ң м–‘мқҳ мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„к°Җ мЎҙмһ¬н•Ёмқ„ м•Ң мҲҳ мһҲм—Ҳмңјл©°, м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқкіј лҶ’мқҖ мғҒкҙҖм„ұмқ„ ліҙмқҙлҠ” нҠ№м • нҳ•нғңмқҳ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқ„ нҷ•мқён• мҲҳ мһҲм—ҲлӢӨ.
Abstract
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the relationship between the malocclusion and dental caries in adolescents with permanent dentition. The subjects of the study were 385 adolescents aged 12 to 15 years. Dental Aesthetic Index (DAI) and DMFT index were recorded as clinical indicators of malocclusion and dental caries.
The mean Dental Aesthetic Index (DAI) score of the subjects was 12.42 and the mean DMFT index of the subjects was 2.89. Four students (1.04%) were included in the group of orthodontic treatment mandatory, which signifies the handicapping malocclusion. Moreover, the result of gender-specific analysis of the DAI components observed that the prevalence of midline diastema and mandibular overjet were significantly higher among boys (p < 0.05).
In 7 components (missing teeth, incisal segment crowding, maxillary anterior irregularity, mandibular anterior irregularity, mandibular overjet, anterior openbite, antero-posterior molar relationship) among the 10 DAI components, abnormal groups showed significantly higher DMFT index than normal groups (p < 0.05).
The subjects in the group of definite to handicapping malocclusion (DAI вүҘ 26) showed significantly higher DMFT index than the subjects in the group of minor or no malocclusion (p < 0.01). In addition, the DAI score had significant positive linear correlation with the DMFT index (r = 0.584, p < 0.01).
Consequently, the current findings suggested a positive relationship between the malocclusion and caries prevalence. And several specific types of malocclusion were supposed to be significantly correlated with dental caries.
мң м№ҳм—ҙкё°м—җм„ң нҳјн•©м№ҳм—ҙкё°лҘј кұ°міҗ мҳҒкө¬м№ҳм—ҙкё°м—җ л“Өм–ҙм„ мІӯмҶҢл…„л“Өмқҳ кө¬к°• кұҙк°•мқҖ нҸүмғқ кө¬к°• кұҙк°•мқҳ кё°нӢҖмқҙ лҗҳлҜҖлЎң мқҙ мӢңкё°мқҳ кө¬к°•кұҙк°•кҙҖлҰ¬лҠ” л§Өмҡ° мӨ‘мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ[1]. мІӯмҶҢл…„кё°м—җ л°ңмғқн•ҳлҠ” кө¬к°• м§ҲнҷҳмқҖ лҸҷнҶөмқ„ мң л°ңн• лҝҗл§Ң м•„лӢҲлқј м Җмһ‘мһҘм• лҘј мқјмңјнӮӨкі , м •мғҒм Ғмқё м№ҳм—ҙкіј көҗн•©мқҳ мҷ„м„ұмқ„ л°©н•ҙн• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. 2012л…„ мӢңн–үлҗң м „көӯ н•ҷмғқ кұҙк°•кІҖмӮ¬ кІ°кіј, мҡ°лҰ¬лӮҳлқј мІӯмҶҢл…„мқҳ мЈјмҡ” кө¬к°• м§ҲнҷҳмқҖ м№ҳм•„ мҡ°мӢқмҰқ, м№ҳмЈјм§Ҳнҷҳ, л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мҲңм„ңлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬мңјл©°, лӢЁм—° к°ҖмһҘ лҶ’мқҖ 비мңЁмқ„ м°Ём§Җн•ҳкі мһҲлҠ” м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқмқҖ мЎ°кёҲм”© к°җмҶҢн•ҳкі мһҲлҠ” л°ҳл©ҙ м№ҳмЈјм§Ҳнҷҳкіј л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ 진лӢЁ 비мңЁмқҖ м җм җ лҶ’м•„м§ҖлҠ” 추세лҘј ліҙмқҙкі мһҲлӢӨ[2]. л”°лқјм„ң мқҙ мӢңкё° н•ҷмғқл“Өмқҳ кө¬к°•кұҙк°• мҲҳмӨҖмқ„ мҰқ진 л°Ҹ мң м§Җн•ҳкё° мң„н•ҙм„ңлҠ” м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқмқ„ 비лЎҜн•ң мЈјмҡ” кө¬к°• м§Ҳнҷҳмқҳ л°ңмғқ л°Ҹ мқҙмҷҖ кҙҖл Ёлҗң мҡ”мҶҢл“Өм—җ лҢҖн•ң лӢӨк°Ғм Ғмқё м—°кө¬к°Җ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ.
2012л…„ ліҙкұҙліөм§Җл¶Җм—җм„ң л°ңн‘ңн•ң көӯлҜјкө¬к°•ліҙкұҙмӢӨнғңмЎ°мӮ¬м—җ л”°лҘҙл©ҙ, 1мқё нҸүк· ліҙмң мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” 8м„ём—җм„ң 0.7к°ң, 12м„ём—җм„ң 1.8к°ңмқҙм—Ҳмңјл©°, 15м„ём—җм„ң 3.3к°ңмқҙм—ҲлӢӨ[3]. мқҙлҠ” 12м„ёлҘј кё°мӨҖмңјлЎң н•ҳмҳҖмқ„ л•Ң 2003л…„лҸ„м—җ 3.3к°ң, 2006л…„лҸ„м—җ 2.2к°ң, 2010л…„лҸ„м—җ 2.0к°ңлЎң м җм°Ё к°җмҶҢн•ҳлҠ” 추세мқҙкё°лҠ” н•ҳм§Җл§Ң м•„м§Ғ OECD нҸүк· мқё 1.6к°ңлҘј мӣғлҸ„лҠ” мӢӨм •мқҙл©°, лҢҖл¶Җ분мқҙ 1к°ң лҜёл§Ңмқё OCED м„ м§„көӯл“Өм—җ 비н•ҳл©ҙ м—¬м „нһҲ л§Өмҡ° лҶ’мқҖ мҲҳм№ҳмқҙлӢӨ[4].
мөңк·јк№Ңм§Җ көӯлӮҙм—җм„ң мӢӨмӢңлҗң мІӯмҶҢл…„мқҳ м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ л°ңмғқкіј кҙҖл Ёлҗң м—°кө¬лҠ” мЈјлЎң кө¬к°•кұҙк°•мӢӨнғңмЎ°мӮ¬[5,6]мқҳ нҳ•нғңлЎң мқҙлЈЁм–ҙм§Җкұ°лӮҳ, кө¬к°•кұҙк°•н–үнғң[7,8], мӢқмқҙ мҠөкҙҖ[9], нқЎм—°мқҙлӮҳ мқҢмЈјмҷҖ к°ҷмқҖ кұҙк°•мң„н—ҳн–үмң„[10]мҷҖ м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұм—җ лҢҖн•ҙ лӢӨлЈЁм—ҲлӢӨ. н•ҳм§Җл§Ң м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ л°ңмғқкіј л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқ„ лӢӨлЈ¬ м—°кө¬лҠ” нқ¬мҶҢн•ҳл©°, лӢӨм–‘н•ң л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ м–‘мғҒмқҙлӮҳ мӢ¬лҸ„м—җ л”°лҘё м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ м—җ лҢҖн•ң м—°кө¬лҠ” мқҙлЈЁм–ҙм§Җм§Җ м•ҠмқҖ мӢӨм •мқҙлӢӨ.
мқҙм—җ ліё м—°кө¬лҠ” м ң2лҢҖкө¬м№ҳк№Ңм§Җ кө¬к°• лӮҙм—җ 맹м¶ңн•ҳм—¬ 비көҗм Ғ м•Ҳм •лҗң көҗн•©мқ„ мқҙлЈЁкё° мӢңмһ‘н•ң мҳҒкө¬м№ҳм—ҙкё°мқҳ 12~15м„ё мІӯмҶҢл…„мқ„ лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң, мҡ°лҰ¬лӮҳлқј мІӯмҶҢл…„мқҳ 3лҢҖ кө¬к°• м§Ҳнҷҳм—җ мҶҚн•ҳлҠ” л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мқҳ мғҒнҳё м—°кҙҖм„ұмқ„ м•Ңм•„ліҙкі мһҗ н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. нҠ№нһҲ, л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мӢ¬лҸ„м—җ л”°лҘё м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мқҳ м°ЁмқҙмҷҖ м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмқ„ мң л°ңн•ҳкё° мү¬мҡҙ нҠ№м • нҳ•нғңмқҳ л¶Җм •көҗн•©м—җ лҢҖн•ҙ мЎ°мӮ¬ 분м„қн•ҳм—¬ к·ё кІ°кіјлҘј ліҙкі н•ҳкі мһҗ н•ңлӢӨ.
2013л…„ 8мӣ”л¶Җн„° 9мӣ”к№Ңм§Җ кө¬к°•кІҖ진мқ„ мӢңн–үн•ң мқөмӮ°мӢң мҶҢмһ¬ 2к°ң мӨ‘н•ҷкөҗ н•ҷмғқ 433лӘ…мқ„ лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмқ„ нҸүк°Җн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢлҘј л°ӣмқҖ кІҪн—ҳмқҙ мһҲкұ°лӮҳ нҳ„мһ¬ көҗм • м№ҳлЈҢ мӨ‘мқё кІҪмҡ°, кө¬мҲңкө¬к°ңм—ҙкіј к°ҷмқҖ м•…м•Ҳл©ҙ кё°нҳ•мқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н•ҳкұ°лӮҳ кө¬к°• лӮҙ мң м№ҳк°Җ мһ”мЎҙн•ҳлҠ” кІҪмҡ° л“ұ нҸүк°Җ кё°мӨҖм—җ л¶Җн•©н•ҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ” н•ҷмғқ мҙқ 48лӘ…мқ„ м ңмҷён•ң 385лӘ… мӨ‘ лӮЁн•ҷмғқмқҙ 218лӘ…(56.6%), м—¬н•ҷмғқмқҙ 167лӘ…(43.4%)мқҙм—ҲлӢӨ. мғқл…„мӣ”мқјмқ„ кё°мӨҖмңјлЎң н•ң м—°л №лі„ 분нҸ¬лҠ” 12~15м„ёлЎң, 12м„ёк°Җ 42лӘ…(10.9%), 13м„ёк°Җ 94лӘ…(24.4%), 14м„ёк°Җ 129лӘ…(33.5%), 15м„ёк°Җ 120лӘ…(31.2%)мқҙм—ҲлӢӨ(Table 1).
л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқ„ нҸүк°Җн•ҳкё° мң„н•ң м§Җн‘ңлЎңлҠ” JennyмҷҖ Cons[11]к°Җ кі м•Ҳн•ң м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ(Dental Aesthetic Index; DAI)лҘј мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳм—җ л”°лҘё л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мӢ¬лҸ„мҷҖ көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢ н•„мҡ”лҸ„лҠ” Jenny л“ұ[12]мқҙ кі м•Ҳн•ң л°©лІ•мқ„ кё°мӨҖмңјлЎң 분лҘҳн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ(Table 2).
мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мқ„ нҸүк°Җн•ҳкё° мң„н•ң м§Җн‘ңлЎңлҠ” мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳ(DMFT index)лҘј мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. мҡ°мӢқм—җ лҢҖн•ң кІҖмӮ¬ л°Ҹ 진лӢЁ кё°мӨҖмқҖ 2012л…„ ліҙкұҙліөм§Җл¶Җм—җм„ң л°ңк°„н•ң көӯлҜјкө¬к°•кұҙк°•мӢӨнғңмЎ°мӮ¬ кө¬к°•кІҖ진м§Җм№Ём„ң[3]лҘј м°ёмЎ°н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
л‘җ лӘ…мқҳ м№ҳкіјмқҳмӮ¬к°Җ м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳмҷҖ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳ мёЎм •мқ„ мң„н•ң нӣҲл Ём—җ м°ём—¬н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. л‘җ мЎ°мӮ¬мһҗлҠ” м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳмҷҖ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳмқҳ кі„мёЎ л°©лІ•м—җ лҢҖн•ң мӮ¬м „ көҗмңЎмқ„ л°ӣмқҖ л’Ө м—°кө¬ лҢҖмғҒкіј мң мӮ¬н•ң мЎ°кұҙмқҳ м„қкі лӘЁнҳ• мғҒм—җм„ң кі„мёЎ нӣҲл Ёмқ„ мӢңн–үн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. мқҙ нӣ„, 30к°ңмқҳ л¬ҙмһ‘мң„лЎң м„ нғқлҗң м„қкі лӘЁнҳ•мқ„ лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң л‘җ мЎ°мӮ¬мһҗк°Җ к°Ғк°Ғ 2мЈј к°„кІ©мңјлЎң л°ҳліө кі„мёЎн•ҳлҠ” мҳҲ비 мЎ°мӮ¬лҘј мӢӨмӢңн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. мқҙлҘј нҶөн•ҙ мөңмў…м ҒмңјлЎң кёүлӮҙмғҒкҙҖкі„мҲҳ(Intraclass Correlation Coefficient; ICC) 0.8 мқҙмғҒмқҳ мЎ°мӮ¬мһҗ лӮҙ мқјм№ҳлҸ„мҷҖ мЎ°мӮ¬мһҗ к°„ мқјм№ҳлҸ„лҘј м–»мқҖ л’Ө ліё мЎ°мӮ¬лҘј мӢңн–үн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. ліё мЎ°мӮ¬м—җм„ңлҸ„ мЎ°мӮ¬мһҗ к°„ кі„мёЎмқҳ мһ¬нҳ„м„ұмқ„ нҸүк°Җн•ҳкё° мң„н•ҙ л‘җ мЎ°мӮ¬мһҗк°Җ к°Ғмһҗ кІҖ진н•ң н•ҷмғқл“Ө мӨ‘ л¬ҙмһ‘мң„лЎң 15лӘ…мқ„ м„ л°ңн•ҳм—¬ мҙқ 30лӘ…м—җ лҢҖн•ҙ мқҙмӨ‘ кІҖмӮ¬лҘј мӢӨмӢңн•ҳмҳҖмңјл©°, м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳмқҳ кёүлӮҙмғҒкҙҖкі„мҲҳлҠ” 0.981, мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳмқҳ кёүлӮҙмғҒкҙҖкі„мҲҳлҠ” 0.953мңјлЎң лҶ’мқҖ мқјм№ҳлҸ„лҘј ліҙм—¬ мЎ°мӮ¬ кІ°кіјмқҳ мӢ лў°лҸ„к°Җ мқём •лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ(Table 4).
лӘЁл“ 분м„қмқҖ мңҲлҸ„мҡ°мҡ© SPSS(ver.18, IBM, U.S.A.)лҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҳмҳҖмңјл©° нҶөкі„ мң мқҳмҲҳмӨҖмқҖ 5%лЎң м„Өм •н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
м—°л №лі„ м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳмқҳ м°ЁмқҙлҘј кІҖм •н•ҳкі мһҗ мқјмӣҗ분мӮ°л¶„м„қмқ„ мӢӨмӢңн•ҳмҳҖмңјл©°, к°Ғ м—°л №лі„ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” к·ё 분нҸ¬к°Җ м •к·ңм„ұмқ„ л§ҢмЎұн•ҳм§Җ лӘ»н•ҳм—¬ 비лӘЁмҲҳ нҶөкі„кё°лІ•мқё Kruskal-Walis ANOVA testлҘј мӢӨмӢңн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. м„ұлі„ м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳмҷҖ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” лҸ…лҰҪн‘ңліё t-кІҖм •мқ„ мӢӨмӢңн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳлҘј кө¬м„ұн•ҳлҠ” к°Ғ 10к°ң н•ӯлӘ©мқҳ м„ұлі„м—җ л”°лҘё м°ЁмқҙлҘј кІҖм •н•ҳкё° мң„н•ҙ м№ҙмқҙм ңкіұкІҖм •мқ„, к°Ғ н•ӯлӘ©кіј мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳмҷҖмқҳ м°ЁмқҙлҘј кІҖм •н•ҳкё° мң„н•ҙ лҸ…лҰҪн‘ңліё t-кІҖм •мқ„ мӢңн–үн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. мҡ°мӢқмқҳ мӢ¬лҸ„м—җ л”°лҘё мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳмқҳ м°ЁмқҙлҘј кІҖм •н•ҳкі мһҗ мқјмӣҗ분мӮ°л¶„м„қ л°Ҹ мӮ¬нӣ„кІҖм •(ScheffГ©analysis)мқ„ мӢӨмӢңн•ҳмҳҖмңјл©°, м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳмҷҖ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ м„ нҳ•мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„лҘј кІҖм •н•ҳкё° мң„н•ҙ Pearsonмқҳ мғҒкҙҖ분м„қмқ„ мӢңн–үн•ҳкі , л¶Җк°Җм ҒмңјлЎң Spearmanмқҳ мҲңмң„мғҒкҙҖ분м„қ кІ°кіјлҘј м°ёкі н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳлҠ” нҸүк· 12.42м җмңјлЎң, м—°л №мқҙлӮҳ м„ұлі„м—җ л”°лҘё м°ЁмқҙлҠ” мң мқҳн•ҳм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳлӢӨ. көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢк°Җ л¶Ҳн•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨкі нҢҗлӢЁлҗҳлҠ” 26м җ лҜёл§Ңмқҙ 363лӘ…(94.28%)мңјлЎң к°ҖмһҘ л§Һм•ҳмңјл©°, 26~30м җмқҙ 14лӘ…(3.64%)мңјлЎң к·ё л’ӨлҘј л”°лһҗкі , 31~35м җкіј 36м җ мқҙмғҒмқҖ к°Ғк°Ғ 4лӘ…(1.04%)мңјлЎң лҸҷмқјн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ(Table 5, 6).
м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳлҘј 10к°ң н•ӯлӘ©мңјлЎң 세분нҷ”н•ҳм—¬ к·ё 분нҸ¬лҘј мӮҙнҺҙліҙм•ҳмқ„ л•Ң, м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҙқмғқмқҙ к°ҖмһҘ л§Һмқҙ л°ңмғқн•ҳлҠ” л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ нҳ•нғңмқё кІғмңјлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬мңјл©°(68.6%), 2 mmлҘј мҙҲкіјн•ҳлҠ” кіјлҸ„н•ң мғҒм•…м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҲҳнҸүн”јк°ңк°Җ к·ё лӢӨмқҢмңјлЎң л§Һмқҙ лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ(63.1%). м„ұлі„м—җ л”°лҘё 분нҸ¬м—җм„ңлҠ” мғҒм•… мӨ‘м Ҳм№ҳ м •мӨ‘мқҙк°ңлҹүкіј н•ҳм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҲҳнҸүн”јк°ңлҹүмқҙ м—¬н•ҷмғқм—җ 비н•ҙ лӮЁн•ҷмғқм—җкІҢм„ң лҚ” лҶ’кІҢ лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬мңјл©°, к·ё м°ЁмқҙлҠ” мң мқҳн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ(Table 7).
мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” нҸүк· 2.89к°ңлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬мңјл©°, мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳк°Җ 1к°ң мқҙмғҒмқё кІҪмҡ°к°Җ 342лӘ…мңјлЎң 88.8%лҘј м°Ём§Җн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. м—°л №лі„ 분нҸ¬м—җм„ңлҠ” 12м„ё н•ҷмғқл“Өмқҳ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳк°Җ нҸүк· 1.72к°ңлЎң к°ҖмһҘ м Ғм—Ҳкі , 15м„ё н•ҷмғқл“Өмқҳ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳк°Җ нҸүк· 3.38к°ңлЎң к°ҖмһҘ л§Һм•ҳлӢӨ. 13м„ё н•ҷмғқл“Өкіј 14м„ё н•ҷмғқл“Өмқҳ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳм—җлҠ” мң мқҳн•ң м°Ёмқҙк°Җ м—Ҷм—ҲмңјлӮҳ лӮҳлЁём§Җ 집лӢЁ к°„ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” мң мқҳн• л§Ңн•ң м°ЁмқҙлҘј лӮҳнғҖлғҲлӢӨ(Table 8).
лӮЁн•ҷмғқмқҳ нҸүк· мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” 2.85к°ң, м—¬н•ҷмғқмқҖ нҸүк· 2.95к°ңлЎң м—¬н•ҷмғқмқҙ лҚ” лҶ’кІҢ лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬мңјлӮҳ к·ё м°ЁмқҙлҠ” мң мқҳн•ҳм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳлӢӨ(Table 9).
м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳлҘј кө¬м„ұн•ҳлҠ” к°Ғ 10к°ң н•ӯлӘ©мқ„ м •мғҒлІ”мЈјлҘј кё°мӨҖмңјлЎң лӮҳлҲ„м–ҙ мқҙл“Өмқҳ нҸүк· мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҘј 비көҗн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. кІ°мҶҗ м№ҳм•„ мҲҳ, м „м№ҳл¶Җ м•…к¶Ғ мҙқмғқлҸ„, мғҒвҲҷн•ҳм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мөңлҢҖ ліҖмң„лҹү, н•ҳм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҲҳнҸүн”јк°ңлҹү, м „м№ҳл¶Җ к°ңл°©көҗн•©, м ң1лҢҖкө¬м№ҳ м „нӣ„л°© кҙҖкі„м—җм„ң м •мғҒлІ”мЈјм—җ мҶҚн•ҳлҠ” 집лӢЁкіј лІ—м–ҙлӮң 집лӢЁ к°„мқҳ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳ м°Ёмқҙк°Җ мң мқҳн•ң кІғмңјлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ(Table 10).
м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 26м җ лҜёл§Ңмқҳ нҸүк· мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” 2.71к°ң мқёлҚ° л°ҳн•ҙ көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢк°Җ л°ҳл“ңмӢң н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨкі нҢҗлӢЁлҗҳлҠ” м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 36м җ мқҙмғҒмқҳ нҸүк· мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” 7.25к°ңлЎң л§Өмҡ° лҶ’кІҢ лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ. л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мӢ¬лҸ„лҘј кё°мӨҖмңјлЎң м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳлҘј 분лҘҳн•ҳмҳҖмқ„ л•Ң, м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 26м җ лҜёл§Ңмқё көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢк°Җ л¶Ҳн•„мҡ”н•ң 집лӢЁмқҳ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” лӮҳлЁём§Җ 집лӢЁмқҳ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳмҷҖ мң мқҳн•ң м°ЁмқҙлҘј ліҙмҳҖмңјлӮҳ, көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢк°Җ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨкі нҢҗлӢЁлҗҳлҠ” м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 26м җ мқҙмғҒмқё 집лӢЁ лӮҙм—җм„ңлҠ” к·ё мӢ¬лҸ„м—җ л”°лҘё м°Ёмқҙк°Җ мң мқҳн•ҳм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳлӢӨ(Table 11).
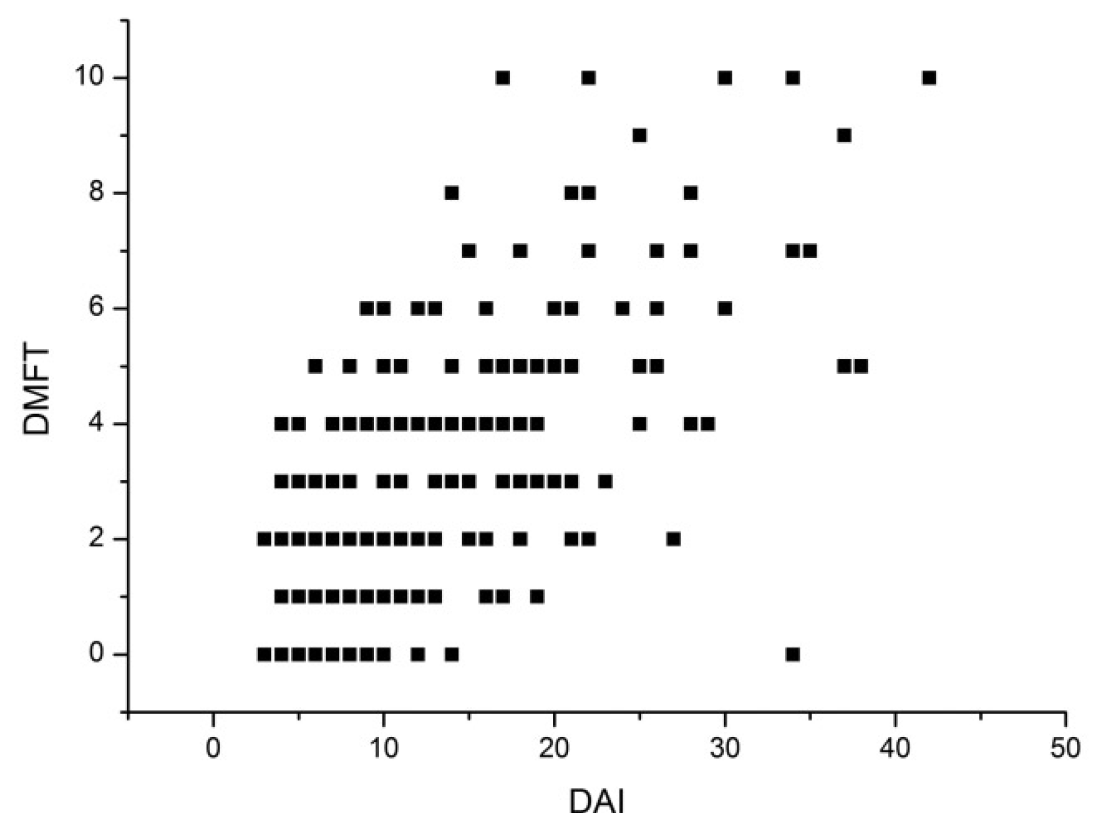
м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳмҷҖ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„лҘј м•Ңм•„ліҙкё° мң„н•ҙ Pearsonкіј Spearmanмқҳ мғҒкҙҖкҙҖ계분м„қмқ„ мӢңн–үн•ң кІ°кіј, мғҒкҙҖкі„мҲҳлҠ” к°Ғк°Ғ 0.584, 0.551лЎң л‘җ кІҪмҡ° лӘЁл‘җ м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳк°Җ нҒҙмҲҳлЎқ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳк°Җ мҰқк°Җн•ҳлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬мңјл©°, л‘җ ліҖмҲҳк°„м—җ м„ңлЎң мң мқҳн•ң м„ нҳ•мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„к°Җ нҷ•мқёлҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ(Table 12, Fig. 1).
м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқмқҖ м№ҳм•„мқҳ кІҪмЎ°м§Ғм—җ л°ңмғқн•ҳлҠ” м§ҲнҷҳмңјлЎң кІҪмЎ°м§Ғ л¬ҙкё°м§Ҳ м„ұ분мқҳ нғҲнҡҢмҷҖ мқҙлҘј л’Өл”°лҘҙлҠ” лӮЁмқҖ мң кё°л¬јм§Ҳмқҳ нҢҢкҙҙк°Җ нҠ№м§•мқҙлӢӨ. м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқмқ„ мқјмңјнӮӨлҠ” мӣҗмқёмңјлЎң 1960л…„лҢҖ мІҳмқҢмңјлЎң м№ҳм•„, м№ҳнғң, мқҢмӢқмқҳ 3лҢҖ мҡ”мҶҢм—җ лҢҖн•ң к°ңл…җмқҙ нҷ•лҰҪлҗҳм—Ҳкі , мқҙнӣ„ м—¬кё°м—җ нғҖм•Ў, л¶ҲмҶҢ, мӮ¬нҡҢ кІҪм ңм Ғ мҡ”мқё, м№ҳм—ҙкіј л¶Җм •көҗн•© л“ұмқҳ лӢӨм–‘н•ң мҡ”мҶҢл“Өмқҙ лҚ§л¶ҷм—¬м ё м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқмқҖ лӢӨмқёмһҗм—җ мқҳн•ң м „м—јм„ұм§ҲнҷҳмқҙлқјлҠ” мҳӨлҠҳлӮ мқҳ к°ңл…җмқҙ м •лҰҪлҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ[14].
м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқм—җ 비н•ҙ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқ„ мӢӨм ңм ҒмңјлЎң м •мқҳн•ҳкі л¶„лҘҳн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҖ м–ҙл Өмҡҙ л¬ём ңмқёлҚ°, мқҙлҠ” л¶Җм •көҗн•©м—җ лҢҖн•ң к°ңк°ңмқёмқҳ мЈјкҙҖм Ғ кҙҖм җ м°Ёмқҙк°Җ м»Өм„ң мқјл°ҳм ҒмңјлЎң мҲҳмҡ©н• мҲҳ мһҲлҠ” м§Җн‘ңлЎң нҷҳмӮ°н•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ н•ңкі„к°Җ мһҲкё° л•Ңл¬ёмқҙлӢӨ[15]. 19м„ёкё° Angle[16]м—җ мқҳн•ҙ кі м•Ҳлҗң л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ 분лҘҳлҠ” мҳӨлҠҳлӮ к№Ңм§ҖлҸ„ нҷҳмһҗлҘј 분м„қн•ҳкі м№ҳлЈҢкі„нҡҚмқ„ мҲҳлҰҪн• л•Ң мң мҡ©н•ҳкІҢ м“°мқҙкі мһҲмңјлӮҳ, м „л°ҳм Ғмқё м№ҳм—ҙ л°Ҹ көҗн•©м–‘мғҒліҙлӢӨлҠ” нҠ№м • мғҒнғңл§Ңмқ„ л°ҳмҳҒн•ҳлҠ” кІҪн–Ҙмқҙ мһҲмңјл©° л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мӢ¬лҸ„лӮҳ көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢмқҳ н•„мҡ”м„ұ л“ұмқ„ л°ҳмҳҒн•ҳм§ҖлҠ” лӘ»н•ҳкё° л•Ңл¬ём—җ м—ӯн•ҷмЎ°мӮ¬м—җлҠ” л¶Җм Ғн•©н•ҳлӢӨ[17]. л”°лқјм„ң 20м„ёкё° мӨ‘л°ҳл¶Җн„° кө¬к°•ліҙкұҙн•ҷм Ғ кҙҖм җм—җм„ң көҗм • м№ҳлЈҢ н•„мҡ”м„ұмқ„ нҸүк°Җн• мҲҳ мһҲлҠ” м§Җн‘ңлҘј л§Ҳл Ён•ҳкі мһҗ лӢӨм–‘н•ң м§ҖмҲҳлҘј к°ңл°ңн•ҳкі м Ғмҡ©мӢңнӮӨлҠ” м—°кө¬к°Җ мқҙлЈЁм–ҙмЎҢлӢӨ. к·ё мӨ‘ 1970л…„лҢҖ к№Ңм§ҖлҠ” Draker[18]мқҳ Handicapping Labiolingual Deviation (HLD) index, Grainger[19]мқҳ Treatment Priority Index(TPI), Salzmann[20]мқҳ Handicapping Malocclusion Assessment Record(HMAR) л“ұмқҙ к°ңл°ңлҗҳм–ҙ лӢӨм–‘н•ң м—°кө¬м—җ м Ғмҡ©лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ. к·ёлҰ¬кі 1980л…„лҢҖ мқҙнӣ„ к°ңл°ңлҗң JennyмҷҖ Cons[11]мқҳ Dental Aesthetic Index(DAI)мҷҖ, Brookкіј Shaw[21]мқҳ Index of Orthodontic Treatment Need(IOTN)к°Җ мҳӨлҠҳлӮ к№Ңм§Җ л„җлҰ¬ м“°мқҙкі мһҲлӢӨ[22]. ліё м—°кө¬м—җм„ң мӮ¬мҡ©н•ң м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ(DAI)лҠ” м№ҳм—ҙ мӢ¬лҜёмғҒнғңм—җ мҳҒн–Ҙмқ„ мЈјлҠ” 진лӢЁмҡ”мҶҢлҘј 10к°ң н•ӯлӘ©мңјлЎң м •лҰ¬н•ң л’Ө, к°Ғк°Ғмқҳ н•ӯлӘ©м—җ лҢҖн•ҙ к°ҖмӨ‘м№ҳлҘј кіұн•ҳм—¬ лҚ”н•ң к°’м—җ мғҒмҲҳлҘј лҚ”н•ҳм—¬ кө¬н•ҳлҠ” м§Җн‘ңлЎң, 1997л…„ м„ёкі„ліҙкұҙкё°кө¬м—җм„ң л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқ„ нҸ¬н•Ён•ҳлҠ” м№ҳм—ҙмқҳ мӢ¬лҜём„ұмқ„ нҸүк°Җн•ҳкё° мң„н•ң м§Җн‘ңлЎң 추мІң, кІҖмӮ¬ л°©лІ• л°Ҹ нҢҗм • кё°мӨҖмқ„ м ңмӢңн•ЁмңјлЎңмҚЁ к·ё мӢ лў°м„ұмқ„ мқём •л°ӣмқҖ л°” мһҲлӢӨ[13].
көӯлӮҙм—җм„ңлҠ” 1994л…„ мЎ° л“ұ[23]мқҙ н•ңкөӯмқё 12м„ё м•„лҸҷ 206лӘ…мқҳ мғҒвҲҷн•ҳм•… лӘЁнҳ•мқ„ м ңмһ‘н•ң л’Ө кі„мёЎн•ҳм—¬ мҡ°лҰ¬лӮҳлқј мөңмҙҲлЎң н•ңкөӯмқё 12м„ё м•„лҸҷмқҳ м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳлҘј л°ңн‘ңн•ҳмҳҖлҠ”лҚ° көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢк°Җ л§Өмҡ° н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨкі нҢҗлӢЁлҗҳлҠ” 36м җ мқҙмғҒмқҙ 6.3%лЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ. мқҙнӣ„ 2002л…„ к№Җ л“ұ[24]мқҙ м „лқјл¶ҒлҸ„ м§Җм—ӯмқҳ 12м„ё мІӯмҶҢл…„ 242лӘ…кіј 16м„ё мІӯмҶҢл…„ 295лӘ…мқ„ лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң мӢӨмӢңн•ң м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳм—җ лҢҖн•ң м—ӯн•ҷмЎ°мӮ¬м—җм„ңлҠ” 36м җ мқҙмғҒмқҙ 3.9%лҘј м°Ём§Җн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. ліё м—°кө¬м—җм„ңлҠ” 36м җ мқҙмғҒмқё кІҪмҡ°к°Җ м „мІҙ 385лӘ… мӨ‘ 4лӘ…мңјлЎң 1.04% м •лҸ„лҘј м°Ём§Җн•ҳлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ. мқҙмҷҖ к°ҷмқҙ көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢ н•„мҡ”лҸ„к°Җ лҶ’мқҖ мІӯмҶҢл…„мқҳ 비мңЁмқҙ м җм җ к°җмҶҢн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҖ, м•һм„ң м–ёкёүн•ң л‘җ м—°кө¬[23,24]мҷҖ ліё м—°кө¬к°Җ лӘЁл‘җ көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢлҘј л°ӣмқҖ кІҪн—ҳмқҙ мһҲкұ°лӮҳ көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢ мӨ‘мқё н•ҷмғқмқ„ м—°кө¬лҢҖмғҒм—җм„ң м ңмҷён•ҳмҳҖлӢӨлҠ” мёЎл©ҙм—җм„ң ліҙм•ҳмқ„ л•Ң кіјкұ°м—җ 비н•ҙ мҶҢм•„мІӯмҶҢл…„кё°м—җ мЎ°кё° көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢлҘј л°ӣлҠ” кІҪмҡ°к°Җ мҰқк°Җн–Ҳкё° л•Ңл¬ёмқј кІғмқҙлқјкі мғқк°ҒлҗңлӢӨ. 1976л…„м—җм„ң 1979л…„ мӮ¬мқҙ м„ңмҡёлҢҖн•ҷкөҗ м№ҳкіј лҢҖн•ҷлі‘мӣҗ мҶҢм•„м№ҳкіјмқҳ м „мІҙ 진лЈҢм—җм„ң көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢк°Җ м°Ём§Җн•ҳлҠ” 비мңЁмқҙ 3% лҜёл§Ңмқҙм—ҲлҚҳлҚ° л°ҳн•ҙ 2000л…„м—җлҠ” 21.5%, 2008л…„м—җлҠ” 37.5%лЎң мҰқк°Җн•ЁмңјлЎңмҚЁ мҶҢм•„мІӯмҶҢл…„кё° мЎ°кё° көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢмқҳ мҲҳмҡ”к°Җ м җм җ мҰқк°Җн•ҳкі мһҲлӢӨкі л¶„м„қн•ң мҶҗ л“ұ[25]мқҳ м—°кө¬кІ°кіјлҸ„ мқҙлҘј л’·л°ӣм№Ён•ңлӢӨ.
мқҙл ҮкІҢ мҶҢм•„мІӯмҶҢл…„кё° мһҗл…Җм—җкІҢ мЎ°кё° көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢлҘј мӢңн–үн•ҳлҠ” л¶ҖлӘЁлӢҳл“ӨмқҖ көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢлҘј нҶөн•ҙ м•ҲлӘЁмқҳ к°ңм„ кіј мқҙм—җ л”°лҘё мһҗмӢ к°җ нҡҢліөлҝҗл§Ң м•„лӢҲлқј 추нӣ„ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мңјлЎң мқён•ҙ м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқмқҙлӮҳ м№ҳмЈјм§Ҳнҷҳм—җ мқҙнҷҳлҗҳкё° мү¬мҡҙ нҷҳкІҪмқҙ к°ңм„ лҗҳкё°лҘј кё°лҢҖн•ҳлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ[26]. н•ҳм§Җл§Ң, мқјл°ҳм Ғмқё мқёмӢқкіјлҠ” лӢ¬лҰ¬ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҙ м№ҳм•„ мҡ°мӢқмқ„ мң л°ңн•ҳлҠ” мң„н—ҳ мқёмһҗмһ„мқ„ мҰқлӘ…н•ң мһҘкё° мў…лӢЁ м—°кө¬лҠ” м•„м§Ғ лҜёлҜён•ң мӢӨм •мқҙл©°, мқҙмҷҖ кҙҖл Ёлҗң мқҙм „ м—°кө¬л“Өмқҳ мғҒл°ҳлҗң кІ°кіјлЎң л…јлһҖмқҙ м§ҖмҶҚлҗҳм–ҙ мҷ”лӢӨ[27].
GГЎbris л“ұ[28]мқҖ 15~18м„ё мІӯмҶҢл…„ 483лӘ…мқ„ лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң н•ң м—°кө¬м—җм„ң м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 26м җ мқҙмғҒмқё 집лӢЁмқҳ нҸүк· мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳк°Җ 8.0к°ңмқёлҚ° л°ҳн•ҙ м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 26м җ лҜёл§Ңмқё 집лӢЁмқҳ нҸүк· мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” 6.06к°ңлЎң л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҙ мһҲлҠ” кІҪмҡ°к°Җ к·ёл Үм§Җ м•ҠмқҖ кІҪмҡ°м—җ 비н•ҙ мң мқҳн•ҳкІҢ лҶ’мқҖ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмңЁмқ„ ліҙмқёлӢӨкі н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. Nobile л“ұ[29]лҸ„ л¬ҙмһ‘мң„лЎң 추м¶ңлҗң 11~15м„ё мІӯмҶҢл…„ 1000лӘ…мқ„ лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң н•ң м—°кө¬м—җм„ң лҶ’мқҖ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҘј лӮҳнғҖлӮјмҲҳлЎқ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мӢ¬лҸ„к°Җ мҰқк°Җн•ҳм—¬ л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмқҙ м„ңлЎң мң мқҳн•ң м—°кҙҖкҙҖкі„лҘј к°Җ진лӢӨкі мЈјмһҘн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
л°ҳл©ҙ, мқҙмҷҖ мғҒл°ҳлҗң мқҳкІ¬лҸ„ мһҲлӢӨ. Helmкіј Petersen[30]мқҖ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҙ мһҲлҠ” 176лӘ…мқ„ 22л…„к°„ 추м Ғ мЎ°мӮ¬н•ң кІ°кіј л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј мҡ°мӢқмң лі‘мңЁ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ м–ҙл– н•ң м—°кҙҖм„ұлҸ„ м°ҫмқ„ мҲҳ м—Ҷм—ҲлӢӨкі н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. Palin-PalokasмҷҖ Ruokokoski-Pirkkanen[31]лҠ” л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј м№ҳм•„ мҡ°мӢқмқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұм—җ лҢҖн•ң л¬ён—Ң кі м°° кІ°кіј, мҡ°мӢқмңјлЎң мқён•ҙ мғҒмӢӨлҗң мҳҒкө¬м№ҳ кіөк°„м—җ м Ғм Ҳн•ң кіөк°„мң м§Җк°Җ мқҙлЈЁм–ҙм§Җм§Җ м•Ҡм•„м„ң л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҙ мң л°ңлҗ мҲҳлҠ” мһҲмңјлӮҳ к·ё м—ӯмқҖ мҰқлӘ…лҗҳм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳлӢӨкі н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. Thomson[32]мқҖ 1972л…„м—җм„ң 1973л…„ мӮ¬мқҙм—җ кө¬к°•кІҖ진мқ„ мӢңн–үн•ң 12м„ё м–ҙлҰ°мқҙ 1037лӘ… мӨ‘ 15м„ё, 18м„ё, 26м„ёк№Ңм§Җ 추м Ғ мЎ°мӮ¬к°Җ мқҙлЈЁм–ҙ진 452лӘ…мқ„ лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң көҗм • м№ҳлЈҢ мң л¬ҙм—җ л”°лҘё кө¬к°• кұҙк°• мғҒнғңлҘј 비көҗн•ң мҪ”нҳёнҠё м—°кө¬ кІ°кіјлҘј л°ңн‘ңн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. м№ҳм•„ мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мқҳ м°ЁмқҙлҘј кІҖмҰқн•ҳкё° мң„н•ҙ 18м„ёмҷҖ 26м„ём—җ к°Ғк°Ғ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳл©ҙмҲҳ(DMFS index)лҘј мЎ°мӮ¬н•ң л’Ө көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢлҘј л°ӣмқҖ кІҪмҡ°мҷҖ л°ӣм§Җм•ҠмқҖ кІҪмҡ°лҘј 비көҗн•ң кІ°кіј л‘җ 집лӢЁ мӮ¬мқҙм—җ мң мқҳн•ң м°ЁмқҙлҘј л°ңкІ¬н• мҲҳ м—Ҷм—ҲлӢӨкі л°қнһҲл©° л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұм—җ лҢҖн•ҙ л¶Җм •м Ғмқё мһ…мһҘмқ„ лӮҳнғҖлғҲлӢӨ.
ліё м—°кө¬м—җм„ңлҠ” м „мІҙм ҒмңјлЎң л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мӢ¬лҸ„мҷҖ м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мӮ¬мқҙм—җ м–‘мқҳ мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„к°Җ нҷ•мқёлҗЁмңјлЎңмҚЁ GГЎbris л“ұ[28], Baskaradoss л“ұ[33]кіј мң мӮ¬н•ң кІ°кіјлҘј ліҙмҳҖмңјл©°, Pearsonмқҳ мғҒкҙҖкі„мҲҳк°Җ 0.584(p < 0.01)лЎң л‘ҳ мӮ¬мқҙм—җ мң мқҳн•ң м„ нҳ• мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„к°Җ мЎҙмһ¬н•ҳлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ. лҳҗ, көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢк°Җ л¶Ҳн•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨкі нҢҗлӢЁлҗҳлҠ” м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 26 лҜёл§Ңмқё 집лӢЁм—җ 비н•ҙ мӨ‘л“ұлҸ„ мқҙмғҒмқҳ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мңјлЎң көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢк°Җ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨкі нҢҗлӢЁлҗҳлҠ” м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 26 мқҙмғҒмқё 집лӢЁмқҳ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳк°Җ мң мқҳн•ң м°ЁмқҙлҘј ліҙмқҙл©° лҶ’кІҢ лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ. м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 26 мқҙмғҒмқё 집лӢЁ лӮҙм—җм„ңлҠ” л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мӢ¬лҸ„к°Җ мҰқк°Җн• мҲҳлЎқ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҸ„ мҰқк°Җн•ҳлҠ” кІҪн–Ҙмқҙ лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬мңјлӮҳ, к·ё м°Ёмқҙк°Җ нҶөкі„м ҒмңјлЎң мң мқҳн•ҳм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳлӢӨ. л”°лқјм„ң ліё м—°кө¬м—җм„ңлҠ” л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мң л¬ҙмҷҖ мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ лҡңл ·н•ң мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„к°Җ мҰқлӘ…лҗң л°ҳл©ҙ, мӨ‘л“ұлҸ„ мқҙмғҒмқҳ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н• л•Ң к·ё мӢ¬лҸ„мҷҖ мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқҖ мҰқлӘ…н•ҳм§Җ лӘ»н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. мқҙлҠ” м „мІҙ м—°кө¬ лҢҖмғҒ мӨ‘ мӨ‘л“ұлҸ„ мқҙмғҒмқҳ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н•ҳлҠ” м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 26 мқҙмғҒмқё кІҪмҡ°к°Җ 22лӘ…(5.72%)м—җ л¶Ҳкіјн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨлҠ” м җм—җм„ң к·ё м—°кҙҖм„ұмқ„ мҰқлӘ…н•ҳкё°м—җлҠ” л¶Ҳ충분н–Ҳмқ„ мҲҳ мһҲмңјл©°, л”°лқјм„ң 추нӣ„ ліҙлӢӨ л§ҺмқҖ мҲҳмқҳ н‘ңліёмқ„ лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң н•ң м—°кө¬к°Җ н•„мҡ”н• кІғмңјлЎң мғқк°ҒлҗңлӢӨ.
Stahlкіј Grabowski[34]лҠ” 7~10м„ё нҳјн•©м№ҳм—ҙкё° м•„лҸҷ 7,639лӘ…мқ„ лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң н•ң м—°кө¬ кІ°кіј л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҙ м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ кіј м—°кҙҖмқҙ мһҲлӢӨкі мқјл°ҳнҷ” н•ҳкё°лҠ” м–ҙл Өмҡ°лӮҳ лӘҮ к°Җм§Җ нҠ№м • нҳ•нғңмқҳ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҖ м№ҳм•„ мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ кіј кҙҖл Ёмқҙ мһҲлӢӨкі н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. мҡ°мӢқ кІҪн—ҳмқҙм—ҶлҠ” 집лӢЁм—җ 비н•ҙ мҡ°мӢқ кІҪн—ҳмқҙ мһҲлҠ” 집лӢЁм—җм„ң н•ҳм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҲҳнҸүн”јк°ңлҹүмқҙ нҳ„м Җн•ҳкІҢ лҶ’кІҢ лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨлҠ” м җмқҖ ліё м—°кө¬ кІ°кіјмҷҖ мң мӮ¬н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. н•ҳм§Җл§Ң м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҙқмғқ, мғҒм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҲҳнҸүн”јк°ңлҹү, 2кёү 2лҘҳ л¶Җм •көҗн•© л“ұмқҖ мҡ°мӢқ кІҪн—ҳмқҳ мң л¬ҙм—җ л”°лҘё м°Ёмқҙк°Җ м—Ҷм—ҲлӢӨкі н•ҳмҳҖмңјл©°, мқҙлҠ” м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҙқмғқкіј мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳ мӮ¬мқҙм—җ лҶ’мқҖ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқҙ мһҲлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮң ліё м—°кө¬ кІ°кіјмҷҖ мқјл¶Җ м°ЁмқҙлҘј ліҙмҳҖлӢӨ.
кіөк°„ л¶ҖмЎұмңјлЎң мқён•ң мҙқмғқмқҙлӮҳ лҳҗлҠ” лӢӨлҘё мӣҗмқёмңјлЎң мқён•ҙ лӮҳнғҖлӮҳлҠ” л¶Ҳк·ңм№ҷн•ң м№ҳм—ҙмқҖ м Җмһ‘м—җ мқҳн•ҙ мқјм–ҙлӮҳлҠ” мһҗм •мһ‘мҡ©мқ„ м Җн•ҙн• лҝҗл§Ң м•„лӢҲлқј 칫мҶ”м§Ҳм—җ мқҳн•ң кө¬к°•мң„мғқкҙҖлҰ¬лҘј м–ҙл өкІҢ н•ҳкё° л•Ңл¬ём—җ м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқмқ„ мң л°ңн•ҳкё° мү¬мҡҙ мҡ”мқёмңјлЎң мқёмӢқлҗҳм–ҙ мҷ”лӢӨ[14]. ліё м—°кө¬м—җм„ң кІ°мҶҗм№ҳм•„к°Җ мЎҙмһ¬н•ҳкұ°лӮҳ н•ң м•…к¶Ғ мқҙмғҒм—җ мҙқмғқмқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н•ҳлҠ” кІҪмҡ°, мғҒм•… лҳҗлҠ” н•ҳм•… м „м№ҳ мӨ‘ м•…к¶Ғм—җм„ң к°ҖмһҘ л§Һмқҙ ліҖмң„лҗң м№ҳм•„мқҳ ліҖмң„лҹүмқҙ 1 mm лҘј мҙҲкіјн•ҳлҠ” кІҪмҡ°к°Җ к·ёл Үм§Җ м•ҠмқҖ кІҪмҡ°ліҙлӢӨ нҸүк· мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳк°Җ лҶ’кІҢ лӮҳнғҖлӮң кІғмқҖ мң„мҷҖ к°ҷмқҖ к°Җм„Өмқ„ л’·л°ӣм№Ён•ҙ мӨҖлӢӨ. н•ҳм§Җл§Ң Hafez л“ұ[35]мқҖ мҙқмғқкіј м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұм—җ лҢҖн•ҙ лӢӨлЈ¬ 6,914к°ңмқҳ л…јл¬ё мӨ‘ м—°кө¬ мЎ°кұҙм—җ л¶Җн•©н•ҳлҠ” 8к°ң л…јл¬ём—җ лҢҖн•ң мІҙкі„м Ғ л¬ён—Ң кі м°°мқ„ мӢңн–үн•ҳмҳҖлҠ”лҚ°, 8к°ң л…јл¬ё мӨ‘ 4к°ңмқҳ л…јл¬ёмқҖ к·ё м—°кҙҖм„ұмқ„ л°қнҳҖлӮҙм§Җ лӘ»н•ҳмҳҖкі , 2к°ң л…јл¬ёмқҖ мҳӨнһҲл Ө мҙқмғқмқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н• мҲҳлЎқ мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мқҙ лӮ®мқҖ кІғмңјлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬мңјл©°, лӮҳлЁём§Җ 2к°ң л…јл¬ём—җм„ң мҙқмғқкіј мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мӮ¬мқҙм—җ мң мқҳн•ң м–‘мқҳ мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„к°Җ лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬мңјлӮҳ, л…јл¬ёмқҳ м§Ҳмқҙ м „л°ҳм ҒмңјлЎң лӮ®м•„ м§ҖкёҲк№Ңм§Җмқҳ м—°кө¬ кІ°кіјлҘј л°”нғ•мңјлЎң л‘ҳ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқ„ мҰқлӘ…н•ҳлҠ” лҚ°лҠ” н•ңкі„к°Җ мһҲлӢӨкі н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
н•ҳм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҲҳнҸүн”јк°ңлҠ” н•ҳм•… 4м „м№ҳ мӨ‘ 1к°ң мқҙмғҒмқҳ м№ҳм•„к°Җ мғҒм•… м№ҳм•„м—җ 비н•ҙ м „л°©мңјлЎң лҸҢм¶ңлҗң кІҪмҡ°, мҰү м „м№ҳл¶Җ көҗм°Ёкөҗн•©мқ„ мқҳлҜён•ңлӢӨ. м „м№ҳл¶Җ көҗм°Ёкөҗн•©мқҙ л°ңмғқн•ң н•ҳм•… м „м№ҳ мӨ‘ лҸҢм¶ң м •лҸ„к°Җ к°ҖмһҘ мӢ¬н•ң л¶Җ분мқҳ кёёмқҙ(mm)лҘј мёЎм •н•ҳкІҢ лҗҳл©°, көҗм°Ёкөҗн•©мқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н•ҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ” кІҪмҡ°лҠ” 0(mm)мңјлЎң кё°лЎқн•ңлӢӨ. л”°лқјм„ң н•ҳм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҲҳнҸүн”јк°ңлҠ” кіЁкІ©м„ұ 3кёү л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҙкұ°лӮҳ лӢЁмҲңнһҲ м№ҳм•„мқҳ л¶Ҳк·ңм№ҷ н•ң л°°м—ҙлЎң мқён•ң көӯмҶҢм Ғмқё м№ҳм„ұ көҗм°Ёкөҗн•©мқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н•Ёмқ„ мқҳлҜён•ңлӢӨ. ліё м—°кө¬м—җм„ң м „м№ҳл¶Җ көҗм°Ёкөҗн•©мқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н•ҳлҠ” 집лӢЁмқҳ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳк°Җ к·ёл Үм§Җ м•ҠмқҖ 집лӢЁм—җ 비н•ҙ мң мқҳн•ҳкІҢ лҶ’кІҢ лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лҠ”лҚ°, мқҙ мӨ‘ көӯмҶҢм Ғмқё м№ҳм„ұ көҗм°Ёкөҗн•©мқҳ кІҪмҡ° ліё м—°кө¬мқҳ мҙқмғқмқҙлӮҳ м „м№ҳл¶Җ м№ҳм•„ мөңлҢҖ ліҖмң„лҹү л“ұкіј к°ҷмқҖ л§ҘлқҪм—җм„ң н•ҙм„қн• мҲҳ мһҲмқ„ кІғмңјлЎң мғқк°ҒлҗңлӢӨ. н•ңнҺё, 3кёү л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқҖ м•„м§Ғ мҰқлӘ…лҗҳм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳмңјлӮҳ, м•һм„ң м–ёкёүн•ң Stahlкіј Grabowski[34]лҠ” кіЁкІ©м Ғ л¶ҖмЎ°нҷ”лЎң нҸҗкө¬к°Җ л¶Ҳмҷ„м „н•ҳкі нҳҖ мң„м№ҳк°Җ л¶Ҳм•Ҳм •н• кІҪмҡ° кө¬нҳёнқЎмқҙлӮҳ нҳҖ лӮҙл°Җкё°мҷҖ к°ҷмқҖ кө¬к°• м•…мҠөкҙҖмқҙ нҳ•м„ұлҗ мҲҳ мһҲкі , мқҙлҠ” м „м№ҳл¶Җ к°ңкөҗлӮҳ мғҒм•…к¶Ғ нҳ‘м°©мңјлЎң мқён•ң мҙқмғқ л“ұмқ„ мң л°ңн• мҲҳ мһҲмңјлҜҖлЎң, 3кёү л¶Җм •көҗн•©мңјлЎң мқён•ҙ мң л°ңлҗҳлҠ” лӢӨлҘё нҷҳкІҪм Ғ мҡ”мқёмқҙ м№ҳм•„ мҡ°мӢқ л°ңмғқмқ„ мҙү진мӢңнӮ¬ мҲҳ мһҲмқ„ кІғмқҙлқјкі 분м„қн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. мқҙ мҷём—җлҸ„ м •мғҒ көҗн•©мһҗмқҳ м Җмһ‘ нҢЁн„ҙмқҙ мЈјлЎң лҲҲл¬јл°©мҡё(tear-drop)нҳ•нғңлҘј лӮҳнғҖлӮҙлҠ”лҚ° 비н•ҙ кіЁкІ©м„ұ 3кёү л¶Җм •көҗн•©мһҗмқҳ м Җмһ‘ нҢЁн„ҙмқҙ нҠ№м§•м ҒмңјлЎң нҸӯмқҙ мўҒмқҖ мҲҳм§Ғм Ғ нҳ•нғңмқёвҖҳchopping patternвҖҷмқ„ лӮҳнғҖлӮёлӢӨлҠ” м җкіј[36,37], м •мғҒ көҗн•©мһҗм—җ 비н•ҙ кіЁкІ©м„ұ 3кёү л¶Җм •көҗн•©мһҗмқҳ м Җмһ‘ мӢңк°„мқҙ кёёкі м Җмһ‘ нҡЁмңЁмқҖ л–Ём–ҙ진лӢӨлҠ” м—°кө¬ кІ°кіј[38] л“ұмқ„ м°ёкі н–Ҳмқ„ л•Ң, мқҙлҹ¬н•ң м Җмһ‘ нҢЁн„ҙмқҙлӮҳ м Җмһ‘ нҡЁмңЁмқҳ м°Ёмқҙк°Җ мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ м—җ мҳҒн–Ҙмқ„ лҜём№ мҲҳ мһҲмқ„ кІғмңјлЎң мғқк°ҒлҗңлӢӨ. н•ҳм§Җл§Ң нҳ„мһ¬ кіЁкІ©м„ұ 3кёү л¶Җм •көҗн•©мһҗмҷҖ м •мғҒкөҗн•©мһҗ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ м°Ёмқҙм—җ лҢҖн•ҙ лӢӨлЈ¬ м—°кө¬к°Җ кұ°мқҳ м—ҶлҠ” мӢӨм •мқҙлҜҖлЎң, м•һмңјлЎң мқҙмҷҖ кҙҖл Ёлҗң мўҖ лҚ” мӢ¬лҸ„ мһҲлҠ” м—°кө¬лҘј нҶөн•ҙ к·ё м—°кҙҖм„ұ мң л¬ҙмҷҖ мӣҗмқё мҡ”мҶҢ л“ұм—җ лҢҖн•ң 분м„қмқҙ мқҙлЈЁм–ҙм ём•ј н• кІғмқҙлӢӨ.
ліё м—°кө¬м—җм„ң м „м№ҳл¶Җ к°ңл°©көҗн•©мқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н•ҳлҠ” 집лӢЁмқҳ нҸүк· мҡ°мӢқ кІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳк°Җ 5.06к°ңмқҙм—ҲлҚҳлҚ° л°ҳн•ҙ м „м№ҳл¶Җ к°ңл°©көҗн•©мқҙ м—ҶлҠ” 집лӢЁмқҳ нҸүк· мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” 2.70к°ңлЎң м „м№ҳл¶Җ к°ңл°©көҗн•©мқҳ мң л¬ҙм—җ л”°лқј мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ м—җ мң мқҳн•ң м°Ёмқҙк°Җ мһҲлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ. мІӯмҶҢл…„кё°м—җ лӮҳнғҖлӮҳлҠ” м „м№ҳл¶Җ к°ңл°©көҗн•©мқҖ мЈјлЎң мҶҗк°ҖлқҪ л№Ёкё°лӮҳ л№„м •мғҒм Ғмқё м—°н•ҳ, кө¬нҳёнқЎ л“ұмқҳ кө¬к°•м•…мҠөкҙҖмқҙ мһҘкё°к°„ м§ҖмҶҚлҗҳм—Ҳмқ„ л•Ң лӮҳнғҖлӮ мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. л°ҳлҢҖлЎң, мӢ¬н•ң 2кёү лҳҗлҠ” 3кёү л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҙлӮҳ кіјлҸ„н•ң м•…кіЁмқҳ мҲҳм§Ғм„ұмһҘкіј к°ҷмқҖ кіЁкІ©м Ғ мӣҗмқёмңјлЎң м „м№ҳл¶Җ к°ңкөҗк°Җ л°ңмғқн•ҳкІҢ лҗҳл©ҙ м •мғҒм Ғмқё м Җмһ‘ л°Ҹ м—°н•ҳ, л°ңмқҢ л“ұмқҙ м–ҙл өкІҢ лҗҳкі мқҙм—җ лҢҖн•ң м Ғмқ‘мңјлЎң кө¬к°• м•…мҠөкҙҖмқҙ мң л°ңлҗҳм–ҙ м „м№ҳл¶Җ к°ңкөҗлҘј лҚ” мӢ¬нҷ”мӢңнӮӨлҠ” кІ°кіјлҘј мҙҲлһҳн•ҳкё°лҸ„ н•ңлӢӨ[39]. мқҙл Үл“Ҝ нҳҖ лӮҙл°Җкё° м—°н•ҳлӮҳ кө¬нҳёнқЎкіј к°ҷмқҖ кө¬к°• м•…мҠөкҙҖмқҖ м „м№ҳл¶Җ к°ңл°©көҗн•©мқҳ мӣҗмқё лҳҗлҠ” кІ°кіјлЎң лҸҷл°ҳлҗҳм–ҙ лӮҳнғҖлӮҳлҠ” кІҪмҡ°к°Җ л§ҺлӢӨ. л”°лқјм„ң ліё м—°кө¬ кІ°кіјлҠ” м „м№ҳл¶Җ к°ңл°©көҗн•©мқ„ ліҙмқҙлҠ” кІҪмҡ°к°Җ м •мғҒлІ”мң„мқҳ м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҲҳм§Ғн”јк°ңлӮҳ мӢ¬н”јк°ңкөҗн•©мқ„ ліҙмқҙлҠ” кІҪмҡ°м—җ 비н•ҙ нғҖм•Ўмқҳ нқҗлҰ„мқҙ к°җмҶҢн•ҳкі м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмқҙ нҳёл°ңн•ҳлҠ” кІҪн–Ҙмқ„ ліҙмқёлӢӨлҠ” кё°мЎҙмқҳ к°Җм„Өмқ„ л’·л°ӣм№Ён•ҳкі мһҲлӢӨ.
мқҙлІҲ м—°кө¬лҠ” м—°кө¬ лҢҖмғҒмқҙ м „лқјл¶ҒлҸ„ мқөмӮ°мӢңм—җ мң„м№ҳн•ң 2к°ң мӨ‘ н•ҷкөҗм—җ н•ңм •лҗҳм–ҙ мһҲлӢӨлҠ” м җкіј, нҡЎлӢЁм—°кө¬(cross-sectional study)лЎң л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мқҳ ліҖнҷ” м–‘мғҒмқҖ л°ҳмҳҒлҗҳм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳлӢӨлҠ” м җм—җм„ң н•ңкі„лҘј к°Җм§Җкі мһҲлӢӨ. көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢлҘј л°ӣмқҖ м Ғмқҙ мһҲкұ°лӮҳ көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢ мӨ‘мқё н•ҷмғқмқҖ м—°кө¬лҢҖмғҒм—җм„ң м ңмҷёлҗҳм—ҲлҠ”лҚ°, мӢ¬н•ң л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н•Ём—җлҸ„ көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢлҘј л°ӣм§Җ м•ҠмқҖ кІҪмҡ° м „л°ҳм Ғмқё Dental IQк°Җ лӮ®кұ°лӮҳ мӮ¬нҡҢкІҪм ңм Ғмҡ”мқёмқҙ мҳҒн–Ҙмқ„ лҜёміӨмқ„ к°ҖлҠҘм„ұмқҙ мһҲкё° л•Ңл¬ём—җ мқҙ лҳҗн•ң ліё м—°кө¬ кІ°кіјмқҳ н•ңкі„м җмңјлЎң мғқк°ҒлҗңлӢӨ. мӢӨм ңлЎң Holmes[40]лҠ” нҷҳм•„ ліёмқёмқҳ кө¬к°•ліҙкұҙмқёмӢқлҸ„мҷҖ л¶ҖлӘЁмқҳ м—°л № л°Ҹ көҗмңЎ мҲҳмӨҖ, м§Ғм—…, кұ°мЈј м§Җм—ӯмқҳ нҠ№м„ұмқҙ көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢ н•„мҡ”м„ұм—җ лҢҖн•ң мқёмӢқм—җ мҳҒн–Ҙмқ„ лҜём№ңлӢӨкі н•ҳмҳҖмңјл©°, к№Җ л“ұ[41]мқҖ м–ҙлЁёлӢҲмқҳ кө¬к°•ліҙкұҙмқёмӢқлҸ„мҷҖ м•„лІ„м§Җмқҳ м§Ғм—…мқҙ мһҗл…Җмқҳ көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢ мӢңмһ‘ мӢңкё°м—җ мҳҒн–Ҙмқ„ лҜём№ңлӢӨкі ліҙкі н•ң л°” мһҲлӢӨ. н•ҳм§Җл§Ң мқҙлҹ¬н•ң мҳҲмғҒлҗҳлҠ” н•ңкі„м җм—җлҸ„ л¶Ҳкө¬н•ҳкі , Thilander л“ұ[42]мқҖ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мң лі‘лҘ кіј кҙҖл Ёлҗң м—°кө¬лҠ” көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢ кІҪн—ҳмқҙ м—ҶлҠ” кІҪмҡ°л§Ңмқ„ лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң н•ҙм•јн•ңлӢӨкі н•ҳмҳҖмңјл©°, ліё м—°кө¬мҷҖ мң мӮ¬н•ң м„ н–ү м—°кө¬л“Ө лҳҗн•ң көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢ кІҪн—ҳмқҙ мһҲмқ„ кІҪмҡ° м—°кө¬лҢҖмғҒм—җм„ң м ңмҷён•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ[28,29,33,34]. лҳҗ, ліё м—°кө¬м—җм„ң л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мӢ¬лҸ„лҘј нҸүк°Җн•ҳкё° мң„н•ң м§Җн‘ңлЎң мӮ¬мҡ©н•ң м№ҳм•„мӢ¬ лҜём§ҖмҲҳ(DAI)лҠ” нҳ‘мёЎкөҗм°Ёкөҗн•©мқҙлӮҳ м •мӨ‘м„ ліҖмң„, м „м№ҳл¶Җ кіјк°ңкөҗн•© л“ұмқҳ мқјл¶Җ нҠ№м„ұмқ„ нҸүк°Җн• мҲҳ м—ҶлӢӨлҠ” лӢЁм җмқҙ мһҲлӢӨ. м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқмқҳ мң л°ңм—җлҠ” лӢӨм–‘н•ң мҡ”мқёмқҙ мһ‘мҡ©н• мҲҳ мһҲкі мҳӨнһҲл Ө к°ңмқёмқҳ кө¬к°•мң„мғқмҠөкҙҖмқҙлӮҳ мӢқмқҙмҠөкҙҖ л“ұмқҙ лҚ” нҒ° мҳҒн–Ҙмқ„ лҜём№ мҲҳ мһҲкё° л•Ңл¬ём—җ, 추нӣ„ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҙлӮҳ көҗм •м№ҳлЈҢ мң л¬ҙм—җ л”°лҘё мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ ліҖнҷ”лҘј 비көҗ нҸүк°Җн•ҳкё° мң„н•ң мһҘкё°к°„мқҳ мў…лӢЁм—°кө¬лҘј нҶөн•ң 추м ҒмЎ°мӮ¬к°Җ н•„мҡ”н•ҳл©°, м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ мҷём—җ лӢӨлҘё м§Җн‘ңлҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҳм—¬ л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқ„ мўҖ лҚ” лӢӨк°ҒлҸ„лЎң м—°кө¬ 분м„қн• н•„мҡ”м„ұмқҙ мһҲлӢӨкі мғқк°ҒлҗңлӢӨ. л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н•ҳлҠ” мІӯмҶҢл…„мқҳ кө¬к°• мң„мғқ кҙҖлҰ¬ л°Ҹ мҡ°мӢқ мҳҲл°©мқ„ мң„н•ң м Ғк·№м Ғмқё мІҳм№ҳмҷҖ лҚ”л¶Ҳм–ҙ кіөк°„ мҶҢмӢӨмқҙлӮҳ көҗн•© л¶ҖмЎ°нҷ” л“ұмқ„ мң л°ңн• мҲҳ мһҲлҠ” мІӯмҶҢл…„кё°мқҳ м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқм—җ лҢҖн•ң м Ғм Ҳн•ң кҙҖлҰ¬к°Җ мқҙлЈЁм–ҙ진лӢӨл©ҙ, мІӯмҶҢл…„мқҳ кө¬к°•кұҙк°• мҰқ진лҝҗл§Ң м•„лӢҲлқј лҚ” лӮҳм•„к°Җм„ң мқҙмҷҖ кҙҖл Ёлҗң мӮ¶мқҳ м§Ҳ н–ҘмғҒм—җлҸ„ лҸ„мӣҖмқҙ лҗ мҲҳ мһҲмқ„ кІғмқҙлӢӨ.
ліё м—°кө¬лҠ” м ң2лҢҖкө¬м№ҳк№Ңм§Җ кө¬к°• лӮҙм—җ 맹м¶ңн•ҳм—¬ 비көҗм Ғ м•Ҳм •лҗң көҗн•©мқ„ мқҙлЈЁкё° мӢңмһ‘н•ң мҳҒкө¬м№ҳм—ҙкё° мІӯмҶҢл…„мқҳ л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқ„ м•Ңм•„ліҙкі мһҗ, м „лқјл¶ҒлҸ„ мқөмӮ°мӢң мҶҢмһ¬мқҳ 2к°ң мӨ‘н•ҷкөҗ н•ҷмғқ 385лӘ…мқ„ лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң н•ң кө¬к°•кІҖ진мқ„ нҶөн•ҙ м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳмҷҖ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҘј мЎ°мӮ¬н•ҳкі к·ё кІ°кіјлҘј 분м„қн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
мЎ°мӮ¬лҢҖмғҒ мІӯмҶҢл…„мқҳ нҸүк· м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳлҠ” 12.42м җ, нҸүк· мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҠ” 2.89к°ңлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬мңјл©°, м—°л №м—җ л”°лҘё мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳмқҳ м°ЁмқҙлҠ” мң мқҳн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳлҘј кө¬м„ұн•ҳлҠ” 10к°ң н•ӯлӘ© мӨ‘ 7к°ң н•ӯлӘ©(кІ°мҶҗ м№ҳм•„ мҲҳ, м „м№ҳл¶Җ м•…к¶Ғ мҙқмғқлҸ„, мғҒм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мөңлҢҖ ліҖмң„лҹү, н•ҳм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мөңлҢҖ ліҖмң„лҹү, н•ҳм•… м „м№ҳл¶Җ мҲҳнҸүн”јк°ңлҹү, м „м№ҳл¶Җ к°ңл°©көҗн•©, м ң1лҢҖкө¬м№ҳмқҳ м „нӣ„л°© кҙҖкі„)мқҙ м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқ мң лі‘лҘ кіј мң мқҳн•ң кҙҖкі„к°Җ мһҲлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ. лҳҗ, лӘ…л°ұн•ң л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мЎҙмһ¬к°Җ мқём •лҗҳлҠ” м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ 26м җмқ„ кё°мӨҖмңјлЎң, 26м җ лҜёл§Ңм—җ 비н•ҙ 26м җ мқҙмғҒмқё 집лӢЁмқҳ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳк°Җ лҶ’кІҢ лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬мңјл©°, м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳмҷҖ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳ мӮ¬мқҙм—җ мң мқҳн•ң м–‘мқҳ м„ нҳ• мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„лҘј нҶөн•ҙ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқҳ мӢ¬лҸ„к°Җ лҶ’м•„м§ҲмҲҳлЎқ мҡ°мӢқкІҪн—ҳмҳҒкө¬м№ҳм§ҖмҲҳлҸ„ мҰқк°Җн•ҳлҠ” кІҪн–Ҙмқҙ мһҲмқҢмқ„ нҷ•мқён•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
мқҙмғҒмқҳ кІ°кіјлЎңл¶Җн„° мІӯмҶҢл…„мқҳ л¶Җм •көҗн•©кіј м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқ мң лі‘лҘ мӮ¬мқҙм—җ мң мқҳн•ң м–‘мқҳ мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„к°Җ мЎҙмһ¬н•Ёмқ„ м•Ң мҲҳ мһҲм—Ҳмңјл©°, м№ҳм•„мҡ°мӢқмҰқкіј лҶ’мқҖ мғҒкҙҖм„ұмқ„ ліҙмқҙлҠ” нҠ№м • нҳ•нғңмқҳ л¶Җм •көҗн•©мқ„ нҷ•мқён• мҲҳ мһҲм—ҲлӢӨ. н–Ҙнӣ„ м№ҳм•„мӢ¬лҜём§ҖмҲҳ мҷём—җ лӢӨм–‘н•ң нҸүк°Җм§Җн‘ңлҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ң м—°кө¬мҷҖ мқҙлҘј л’·л°ӣм№Ё н• мҲҳ мһҲлҠ” мһҘкё°к°„мқҳ 추м ҒмЎ°мӮ¬к°Җ н•„мҡ”н• кІғмңјлЎң мғқк°ҒлҗңлӢӨ.
Fig.В 1.
Scatter plot of Dental Aesthetic Index versus DMFT index according to the Pearson's correlation. R2 = 0.342
TableВ 1.
Age and gender distribution
| N | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 12 | 42 | 10.9 |
| 13 | 94 | 24.4 | |
| 14 | 129 | 33.5 | |
| 15 | 120 | 31.2 | |
| Gender | Male | 218 | 56.6 |
| Female | 167 | 43.4 | |
| Total | 385 | 100 |
TableВ 2.
Severity of malocclusion and orthodontic treatment need categories according to the Dental Aesthetic Index (DAI)
TableВ 3.
The standard DAI regression equation
TableВ 4.
Inter-rater reliability
| Intraclass correlation coefficient (Absolute agreement) | 95% Confidence interval | |
|---|---|---|
| DAI | 0.981** | 0.952~0.996 |
| DMFT | 0.953** | 0.913~0.977 |
TableВ 5.
Distribution of the Dental Aesthetic Index (DAI) score according to age
TableВ 6.
Distribution of the Dental Aesthetic Index (DAI) score according to gender
TableВ 7.
Gender distribution of the Dental Aesthetic Index (DAI) components
| DAI components | Male | Female | Total | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Missing teeth | 0 | 212 | 160 | 372 | |
| 1~4 | 6 | 7 | 13 | ||
| Incisal segment crowding | 0 | 65 | 56 | 121 | |
| 1~2 | 153 | 111 | 264 | ||
| Incisal segment spacing | 0 | 184 | 145 | 329 | |
| 1~2 | 34 | 22 | 56 | ||
| Midline diastema | 0 | 202 | 163 | 365 | * |
| > 0 | 16 | 4 | 20 | ||
| Maxillary anterior irregularity | 0~1 | 106 | 91 | 197 | |
| > 1 | 112 | 76 | 188 | ||
| Mandibular anterior irregularity | 0~1 | 164 | 133 | 297 | |
| > 1 | 54 | 34 | 88 | ||
| Maxillary overjet | 0~2 | 86 | 56 | 142 | |
| > 2 | 132 | 111 | 243 | ||
| Mandibular overjet | 0 | 186 | 157 | 343 | ** |
| > 0 | 32 | 10 | 42 | ||
| Anterior openbite | 0 | 199 | 154 | 353 | |
| > 0 | 19 | 13 | 32 | ||
| Anterior~posterior molar relationship | 0 | 104 | 85 | 189 | |
| 1~2 | 114 | 82 | 196 | ||
| DAI score | < 26 | 205 | 158 | 363 | |
| 26~30 | 8 | 6 | 14 | ||
| 31~35 | 3 | 1 | 4 | ||
| вүҘ 36 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
TableВ 8.
Distribution of the DMFT index according to age
TableВ 9.
Distribution of the DMFT index according to gender
| Gender | Students (N) | DMFT (Mean Вұ SD) | 95% CI for the mean |
|---|---|---|---|
| M | 218 | 2.85 Вұ 2.14 | 2.56~3.13 |
| F | 167 | 2.95 Вұ 2.08 | 2.63~3.27 |
| Total | 385 | 2.89 Вұ 2.11 | 2.68~3.11 |
TableВ 10.
Mean DMFT index of the Dental Aesthetic Index (DAI) components
References
1. Vallejos-SГЎnchez AA, Medina-Solis CE, PГ©rez-Olivares S, et al. : Caries increment in the permanent dentition of Mexican children in relation to prior caries experience on permanent and primary dentitions. J Dent, 34:709-715, 2006.


2. 2012 Annual report of health examination among elementary, middle, and high school students in Korea. Available from URL: http://schoolhealth.kedi.re.kr/Home/Home/SHDataFileDownload.php?GbnCd=SHData&lstnum1=1652&file_seq=1(assesed on Febuary 17, 2014)
3. Korean National Oral Health Survey. Available from URL: >http://www.prism.go.kr/homepage/researchCommon/downloadResearchAttachFile.do?work_key=001&file_type=CPR&seq_no=001&pdf_conv_yn=N&research_id=1351000-201200095 (assessed on Febuary 25, 2014)
4. Construction of the oral health service system for whole life. Available from URL: >http://koix.kisti.re.kr/root_resolution.jsp?koi=KISTI2.1015/RPT.TRKO201000000624 (assessed on Febuary 25, 2014)
5. Kim MK, Han DH, Bae KH : The association between socio-economic status and deciduous dental caries among 3-6 year old children in Pusan. J Korean Acad Dent Health, 30:447-452, 2006.
6. Kwon BM, Bae IH, Kim S, et al. : Dental caries status of 14-16 year old adolescents in Yangsan area. J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent, 41:8-16, 2014.

7. Lee SK : The ratio of tooth surfaces attacked by caries at 12 to 13-year-old students in several cities of Chollabukdo, Korea. J Korean Acad Dent Health, 26:295-302, 2002.
8. Kim SS, Jang JH : Dental health types in middle school students and their Effects on dental caries: focusing on O middle school students in Suwon. J Korean Soc School Health, 13:283-293, 2000.
9. Jang JH : The Relationship of Psychosocial Factors, Dietary Habits and DMFT Index in Adolescents. Korean J Health Educ Promot, 26:23-33, 2009.
10. Jang JH, Kim SH : The relationship of health risk behavior, depression and dental caries experience in 12-year-old adolescents. J Korean Acad Dent Health, 31:593-601, 2007.
11. Jenny J, Cons NC : DAI: The Dental Aesthetic Index. 1st ed.College of Dentistry, University of Iowa, 76-83, 1986.
12. Jenny J, Cons NC, Kohout FJ, Jakobsen J : Predicting handicapping malocclusion using the Dental Aesthetic Index (DAI). Int Dent J, 43:128-132, 1993.

13. Oral health surveys; basic methods. 4th ed. Available from URL: >http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/41905/1/9241544937.pdf(assessed on Febuary 25, 2014)
14. Korean Acad Pediatr Dent : Dentistry for the child and adolesent. 4th ed. Shin-hung international, Seoul, 142-146, 2007.
15. Jung HK, Kuk SH, Kim JK, Kim DK : The improvement of Dental Aesthetic Index (DAI) on orthodontic patient in Korea. J Korean Acad Dent Health, 21:363-378, 1997.
16. Angle EH : Classification of malocclusion. Dent Cosmos, 41:248-264, 1988.
17. Sohn BW, Hwang CJ, Hwang HS : Modality of malocclusion according to regional difference using HLD, TPI, and HMAR. Korean J Orthod, 23:17-35, 1993.
18. Draker HL : Handicapping labio-lingual deviation : A proposed index for public health purpose. Am J Orthod, 46:295-305, 1960.

19. Grainger RM : The orthodontic treatment priority index. Available from URL: >http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/series/sr_02/sr02_025acc.pdf(assessed on March 5, 2014)
20. Salzmann JA : Handicapping Malocclusion Assessment to establish treatment priority. Am J Orthod, 54:749-765, 1968.


21. Brook PH, Shaw WC : The development of an index of orthodontic treatment priority. Eur J Orthod, 16:395-399, 1989.

22. Jenny J, Cons NC : Comparing and contrasting two orthodontic indices, the Index of Orthodontic Treatment Need and the Dental Aesthetic Index. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 110:410-416, 1996.


23. Cho CH, Kang DO, Choi SL, Chang KW : Dental Aesthetic Index (DAI) of 12-year-old Korean adolescent. J Korean Acad Dent Health, 18:103-118, 1994.
24. Kim YS, Lee CH, Kim SG, Chang KW : Dental Aesthetic Index (DAI) of adolescent in Chollabukdo-Province, Korea. J Korean Acad Dent Health, 26:303-312, 2002.
25. Son YJ, Hyun HK, Jang KT, et al. : The changes in practice patterns for the last 8 years (2001-2008) in the department of pediatric dentistry, Seoul National University Dental Hospital. J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent, 37:97-101, 2010.
26. Kiyak HA : Does orthodontic treatment affect patientsвҖҷ quality of life? J Dent Educ, 72:886-894, 2008.


27. Borzabadi-farhani A, Eslamipour F, Asgari I : Association between orthodontic treatment need and caries experience. Acta Odontol Scand, 69:2-11, 2011.


28. GГЎbris K, MГЎrton S, MadlГ©na M : Prevalence of malocclusions in Hungarian adolescents. Eur J Orthod, 28:467-470, 2006.


29. Nobile CG, Pavia M, Fortunato L, Angelillo IF : Prevalence and factors related to malocclusion and orthodontic treatment need in children and adolescents in Italy. Eur J Public Health, 17:637-641, 2007.


30. Helm S, Petersen PE : Causal relation between malocclusion and caries. Acta Odontol Scand, 47:212-221, 1989.

31. Palin-Palokas T, Ruokokoski-Pirkkanen S : Occlusal features and caries experience. Proc Finn Dent Soc, 86:77-82, 1990.

32. Thomson WM : Orthodontic treatment outcomes in the long term: findings from a longitudinal study of New Zealanders. Angle Orthod, 72:449-455, 2002.


33. Baskaradoss JK, Geevarghese A, Rogerm C, Thaliath A : Prevalence of malocclusion and its relationship with caries among school children aged 11- 15 years in southern India. Korean J Orthod, 43:35-41, 2013.


34. Stahl F, Grabowski R : Malocclusion and caries prevalence: is there a connection in the primary and mixed dentitions? Clin Oral Invest, 8:86-90, 2004.

35. Hafez HS, Shaarawy SM, Alsakit AA, Mostafa YA : Dental crowding as a caries risk factor:a systematic review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 142:443-450, 2012.


36. Pröschel P : An extensive classification of chewing patterns in the frontal plane. Cranio, 5:56-63, 1987.

37. Pröschel P, Hofmann M, Spitzer W : Reaction of mastication to occlusal changes induced by correction of mandibular prognathism. J Prosth Dent, 64:211-218, 1990.

38. Sung KH, Sung JH : A comparative study on chewing movement in normal occlusion and skeketal class III malocclulsion. Korean J Orthod, 27:801-813, 1997.
39. Proffit WR, Fields HW, Sarver DM : Contemporary Orthodontics. 5th ed. Mosby, 133-145, 2012.
41. Kim SS, Kim DK, Hwang CJ, Park CY : The effects of related factors and perception of malocclusion on orthodontic treatment timing. J Korean Dent Assoc, 38:452-465, 2000.
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 5,428 View
- 52 Download
- Related articles
-
An Epidemiological Study on the Dental Treatment Needs of Adolescents in Yangsan2016 November;43(4)
Relationship between Obesity and Dental Caries in Primary Teeth in Iksan city2016 May;43(2)
The Prevalence of Malocclusion and Related Self-Esteem of Adolescents in Yangsan2013 November;40(4)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



